Did you know that over 38 million people in the U.S are living with diabetes? It is a condition that requires constant care and attention because blood sugar levels fluctuate regularly. Without proper management, diabetes can further cause complications like heart disease, nerve damage, vision problems and more.
If you have anyone at home with diabetes, you can improve their quality of life by providing them with the right care. But it can only be done if you have the right knowledge about diabetes management.
In this guide, you will gain this knowledge by understanding diabetes types, their associated risks and how to build a practical care routine for your loved ones.
3 Diabetes Types and Key Risks Every Caregiver Should Know
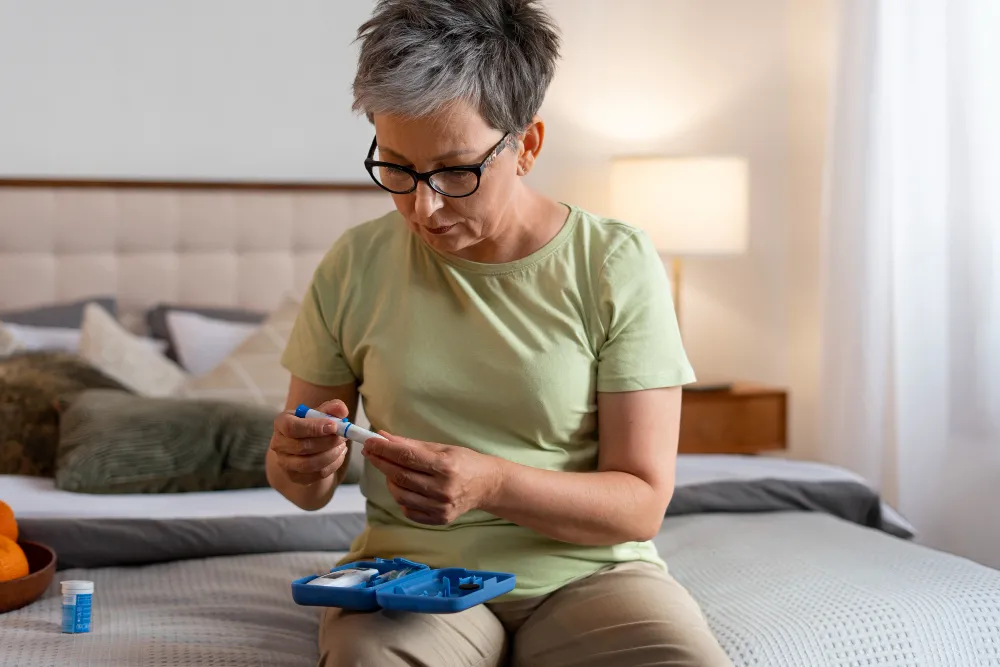

Diabetes has three main types and each of these poses some unique challenges:
1. Type 1
It happens when your body cannot produce insulin. This type of diabetes can develop at any age. About 5-10% of diagnosed cases are Type 1 in the world.
2. Type 2
It is a very common type of diabetes in which the body is unable to use insulin effectively. It accounts for 90-95% of cases.
3. Gestational Diabetes
This type of diabetes occurs in pregnancy and affects 1 in 7 pregnant women globally. It usually resolves after birth but increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Now let’s explore the common health risks associated with each of these diabetes types to ensure proactive management and effective care:
| Type of Diabetes | Health Risks |
| Type 1 Diabetes | Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)- Cardiovascular disease- Nerve damage (neuropathy)- Kidney disease- Eye damage (retinopathy) |
| Type 2 Diabetes | Heart disease- Stroke- High blood pressure- Nerve damage (neuropathy)- Vision problems- Kidney damage |
| Gestational Diabetes | High birth weight in babies- Premature birth- High blood pressure |
A Simple 6-Step Daily Plan for Diabetes Care at Home

As a caregiver, you have an essential role in the diabetic management of your family members. You can follow these practical steps to make things smoother:
1. Monitor Blood Sugar Regularly
Regular monitoring of blood sugar is the most important part of diabetes home care. It helps ensure that blood sugar levels stay within the target range, preventing potential complications like heart disease, nerve damage, and kidney problems.
There are two main ways to do this:
- Glucose Meter: You use this device to prick the patient’s finger to draw a small drop of blood. You can test it on a strip placed in the meter and get an immediate blood sugar reading.
- Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM): This small sensor is placed under the skin of the patient to monitor blood sugar levels continuously. It sends real-time data to the device and helps track changes in blood sugar over time.
Both devices help monitor blood sugar levels in the body but you should consult with a healthcare provider to decide which one works best in your patient’s case.
The typical range for blood sugar level is:
- Fasting blood sugar: Between 70-130 mg/dL
- Post-meal blood sugar: Under 180 mg/dL
If these levels are outside the target range, you should adjust medication or seek emergency care.
2. Plan Balaanced Meals that Support Blood Sugar
Planning balanced meals is another effective step in type 2 diabetes self care. Experts have recommended the “plate method” to support blood sugar levels by balancing meals..
According to this method, you should divide the patient’s plate into three sections:
| Plate Section | What to Include |
| Half of the Plate | Non-starchy vegetables (e.g., leafy greens, broccoli, peppers) |
| One-Quarter of the Plate | Lean proteins (e.g., chicken, fish, turkey) |
| One-Quarter of the Plate | Whole grains or starchy vegetables (e.g., quinoa, sweet potatoes) |
While using these methods, you should ensure that the patient takes three well-balanced meals a day. They should also take some healthy snacks like a handful of nuts or some fruits to maintain their energy levels throughout the day.
3. Make Sure Medications and Insulin Are Taken on Time
Another mandatory step for long-term diabetes management is medication adherence. You should set consistent reminders for medication and insulin doses by using a planner or digital app.
4. Encourage Regular Physical Activity
A light movement, such as a 20-minute walk after meals, can improve blood sugar control. It helps the body use insulin more effectively. It supports heart health which is especially important for individuals with diabetes who are at a higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease.
To make physical exercise a regular part of their routine, you can suggest activities they enjoy, like a short walk in the park or gentle stretching after meals.
5. Be there for Their Mental and Emotional Health too
Diabetes isn’t just a physical condition. It affects emotional health too. To provide emotional support to the patient, make it a point to check in regularly and ask how they’re feeling.
Additionally, encourage your loved one to engage in their hobbies like listening to music or watching a favorite TV show etc. These activities can help reduce stress and enhance their overall well-being.
6. Watch for Warning Signs and Complications
Another important consideration in a care plan for type 2 diabetes is to recognize when something isn’t right with your loved one’s health.
Look out for the following warning signs:
| Warning Sign | What It Could Indicate |
| Extreme fatigue | Could indicate low blood sugar or complications. |
| Confusion or dizziness | A possible sign of blood sugar imbalances. |
| Blurred vision | Can be due to high blood sugar levels. |
| Foot sores or wounds that don’t heal | A potential sign of poor circulation or infection. |
If you notice any of these symptoms, take immediate action like adjusting blood sugar levels or contacting their healthcare provider for advice.
Conclusion
Caring for someone with diabetes at home comes with a big responsibility, but it also lets you have real control over how they feel each day. When you learn about the different types of diabetes and stick to regular routines for checking blood sugar, planning meals, and giving medications, you build a solid base for keeping them healthy.
Plus, having trusted services like Simple Consult there to back you up with expert advice makes everything easier when tough questions come up. This mix of your daily care and getting professional help when needed covers all the bases for managing diabetes well.
FAQs
Mood changes may be linked to fluctuating blood sugar levels. You can ask them to check their blood sugar and consult with their healthcare provider if mood swings persist. Additionally, you can offer emotional support to help them manage stress or frustration.
To prevent hypoglycemia, you should make sure that the patient’s meals are balanced with fiber and healthy carbs. They should not skip meals, and they must also carry glucose tablets or juice for emergencies.
You can manage home care with proper guidance. Diabetes care involves simple tasks that you can learn with resources like online guides or support from healthcare professionals.







Add comment